The company Meraki was founded in 2006 and started out as a research project called Roofnet within MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) which had the aim of providing outdoor Wireless Internet access to the City of Cambridge.

In this article we will discuss the Cisco Meraki brand and answer some Frequently Asked Questions that many people have about Meraki products.
What is Cisco Meraki?
Meraki expanded with the help of investors such as Google and Sequoia and began providing wireless mesh access points and security devices to schools and medium to large sized businesses along with the on-premises software to manage these devices.
In November 2012 the company was purchased by Cisco for $1.2 billion and was re-branded as Cisco Meraki.
The company still provides Wireless Access Points and Security devices but has expanded their portfolio to include Routers, Switches, Cameras and IOT sensors.
The software which is used to manage all these systems was moved into the cloud and Cisco Meraki has become one of the biggest and most respected cloud network companies.
It is the cloud element which sets Cisco Meraki products apart from Cisco’s own line of networking products.
All Cisco Meraki devices are configured and managed solely via the Meraki cloud dashboard and cannot be configured directly through SSH or via a console connection in the same way as a traditional Cisco router or Switch (although there is option to connecting to local configuration pages on each device).
It is this cloud-based, one piece of software to manage everything approach which makes Cisco Meraki devices appealing to companies or organisations such as schools or small businesses, which have small IT departments with limited networking knowledge or limited IT funding.
What is the Cisco Meraki Cloud?
The software which is used to manage and configure Cisco Meraki devices is a web-browser based platform hosted from 8 datacentres located in different parts of the world.
These datacentres form the Meraki cloud and consist of many redundant servers which offer multi-tenancy and contain the network control data for each customer.
The Meraki dashboard is the User front end of the platform which can be accessed through a web browser on a device such as a laptop or desktop computer or through the Meraki App which can be installed on an iPhone or Android device.
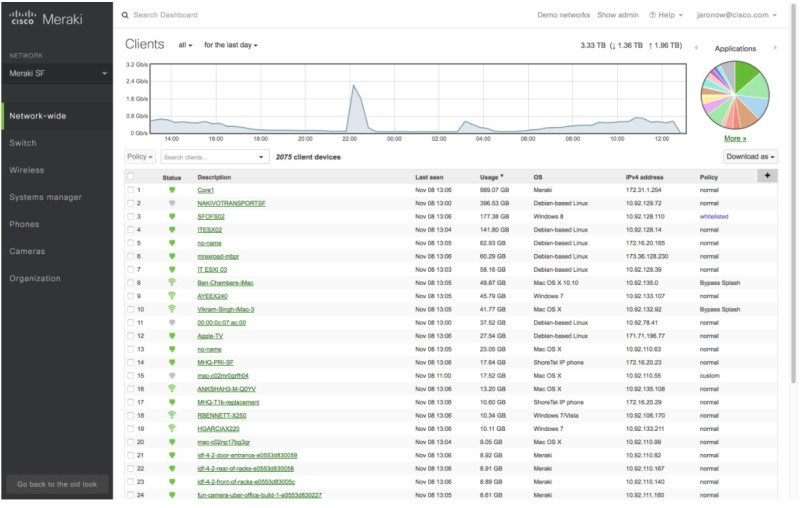
The Meraki dashboard is used to manage every single Meraki device owned by an Organisation.
These devices can be located within any number of sites at any location worldwide and all appear in an organised and structured way in the Meraki dashboard.
This structured approach makes it easy for a small number of Network Administrators to manage multiple sites which may contain many network devices.
The Meraki dashboard is used to monitor, configure, and provide services for all Meraki devices.
Each device is constantly monitored by the dashboard and the network data provided by the devices is gathered and analysed to provide Administrators with information that is not only useful from a Network Admin perspective but can also be used for business analytics.
There are many useful services available to be configured in the Meraki dashboard such as hotspot mapping, contact tracing and asset tracking.
The dashboard is also where product licenses are installed, software upgrades are performed and when needed, support tickets are raised.
In summary the Meraki dashboard is a single piece of software that can be accessed from anywhere and on any device which has a web browser and is used to manage all aspects of a Cisco Meraki network.
Cisco Meraki Main Product Categories
Wireless Access Points
Meraki has a wide range of indoor and outdoor access points some of which can be customised with external antennas to provide coverage to difficult to reach locations.

Each model begins with an MR designation and range from being able to provide basic wireless coverage to high density deployments covering large areas such as auditoriums or stadiums.
The product range covers Wave 2 wireless and the newer WIFI 6.
The MR access points all communicate with the Meraki cloud to receive their configurations which are setup in the Meraki dashboard.
This means that they do not require a separate Wireless Lan Controller to function as the Meraki Cloud acts as the controller.
All end user data is transported on the local network and only the encrypted control traffic for the Access Points is sent to the Meraki Cloud for processing.
Should connectivity fail to the Meraki cloud the access points will continue to serve existing clients but configuration changes to the Access Points or the joining of new devices will not be possible until internet connectivity is restored.
The available Access Point Models are:
Indoor Wave 2 Access Points
MR20 – This model access Point is recommended for SOHO deployments
MR30H – This model access point has the same radio specifications as the MR20 but also includes a 4 port Gigabit switch to allow hardwired connections to the access point.
Outdoor Wave 2 Access Points
MR70 – This model access point is a rugged model which is suitable for outdoor use in areas such as small gardens.
Indoor Wifi 6 Access Points
MR36 – This model is an Entry-level high-performance Wi-Fi 6 AP which has Bluetooth BLE built in for IOT connectivity and Wireless Intrusion Prevention security features. Its maximum data rate is 1.7Gbps.
MR44 – This model is suitable for medium density deployments such as busy offices and offers increased speeds of up to 3Gbps. To support this increased data rate this model AP has a 2.5 Gbps Multigigabit ethernet interface.
MR46E – This model Access Point is suitable for high density deployments and has external connections for the attachment of different types of antennae. This type of access point would be used for buildings which have high ceilings such as warehouses or areas which require directional antennas to be installed such as corridors. The maximum data rate of this AP is 3.5Gbps and has a 2.5Gbps Multigigabit ethernet interface.
MR56 – This is the premium model access point which is recommended for ultra high -density deployments in locations such as University lecture halls or stadiums. It has the largest number of internal radio’s for Multi User – MIMO (Multiple In Multiple Out) with 5.0Gbps data rates. To support these high speeds the hardwired connection to the AP is a 5Gbps Multigigabit Ethernet port.
Outdoor Wifi 6 Access Points
MR76 – This outdoor access point is suitable for deployments such as outdoor campus carparks or industrial point to point links. It has external N-type interchangeable antennas and a maximum data rate of 1.6 Gbps.
MR86 – This access point has been designed to cover high density outdoor deployments or areas with difficult RF coverage. It has the same N-type interchangeable Antenna as the MR76 but is capable of 3.5Gbps speeds.
Switching
Cisco Meraki has a wide range of network switches which are divided into Layer 2 Access Switches, Physically Stackable Switches, Layer 3 Switches and Aggregation switches.

The switch models all start with the MS designation and vary in port density and features. All Cisco Meraki Switches can operate as a virtual stack but only a limited number can operate as a physical stack.
MS-120-8 / MS-120 / MS-125 – These switch models are Layer 2 Access Switches that are suitable for the Small office or Home Office. The MS-120-8 is a compact 8 port switch which is available with or without POE. The MS120 is a larger 24 or 48 port switch with 4 fixed 1Gb Uplink Interfaces which is also available with different POE options. The MS125 is a 24 or 48 port switch which has 4 fixed 10Gb Uplink interfaces and has different POE options available.
MS-210 / MS-225 / MS-250 – These switches are physically stackable switches which are suitable for Branch locations and small offices. They are all available with 24 or 48 ports and have 4 fixed uplink interfaces. The MS-210 has 1 Gb fixed uplinks where the MS225 and MS250 models both have 10Gb SFP+ uplinks. All these switches have the option of an additional redundant power supply and the MS-250 has the addition feature of modular power supplies rather than a fixed internal power supply.
MS-350 / MS-355 / MS-390 – These switches are also physically stackable but are higher end models which are suitable for larger deployments such as campus networks or high-performance networks. This range of switches offer multigigabit interfaces and faster uplink interface speeds compared to the MS-2xx model switches. The MS-390 has a modular uplink which allows 4 or 8 x 10Gb Uplink modules to be installed or 2 x 40Gb QSFP uplinks. The MS350 and MS355 both have fixed uplinks. The MS-350 can be configured as a warm spare (VRRP) for redundancy.
MS-410 / MS-425 / MS450 – These switches are designed for the aggregation layer of a network and only offer SFP+ or QSFP interfaces for fiber connections. These switches are also capable of physical stacking by being joined together from the front uplink modules. These switches all offer redundancy through VRRP when configured as Warm Spares. The power supply on all these models are modular with an optional redundant PSU.
MS-410 – This switch can have either 16 or 32 x GbE SFP interfaces with either 2 or 4 x 10GbE uplinks.
MS-425 – This switch has 16 or 32 x 10GbE SFP+ interfaces with 2 x 40GbE QSFP uplinks.
MS-450 – This switch has the fastest available interfaces compared with all other Meraki switches with 16 x 40GbE QSFP plus interfaces and 2 x 100GbE QSFP28 uplinks.
MDM – Mobile Device Management
The Cisco Meraki MDM is a software tool which can be used to manage the security settings on the endpoints and applications that are joined to the corporate network.
Mobile Device Management tools allow an Administrator to control access to the network or applications based on security policies or device posture and compliance rules.
The Meraki MDM can manage Apple IOS devices, Google Chrome, and Android devices and Microsoft Windows Laptops and Computers.
If a device is non-compliant with the company’s security policies or has been marked as lost or stolen the MDM can be used to prevent that device from accessing the corporate network.
Cellular Gateways
A Cellular Gateway provides a 4G / 5G internet connection which can be used as either a primary WAN service for remote locations or a backup WAN service for critical infrastructure. The Cellular Gateway models all start with the designation MG.
There are 4 models of Cellular Gateway available, two of which have internal antenna and two which have external antenna. All devices have 2 x 1Gbps Ethernet interfaces available for LAN connectivity.
MG21 / MG21E – The MG21 and MG21E both have the same specifications except one model has an internal antenna and the other has an external adjustable antenna for use in areas with poor RF signals. This Model has a single SIM card slot and is a CAT 6 LTE device capable of speeds up to 300Mbps.
MG41 /MG41E – The MG41 and MG11E both have the same specifications except one model has an internal antenna and the other has an external adjustable antenna. This model offers a dual sim card slot and is a CAT 18 LTE device capable of speeds up to 1.2Gbps.
Secure SD-WAN

Cisco Meraki Firewall solutions are marketed as an all-in-one security appliance. These devices are Next Generation hardware firewalls which provide many additional security features and integrated Software Defined WAN functionality.
There are many different models of security appliances available, and each model has the MX designation at the start of the model number.
When simplified there are three main categories of MX.
One which has a small form factor which is more suitable for small branch offices or remote workers and can be sat on a shelf or a desktop.
The second which has a large form factor with an increased number of interfaces which are suitable for much larger networks and would need to be rack mounted.
The last model is a virtual device which is hosted in the cloud and is used for protecting cloud-based applications and cloud infrastructure.
Small Form factor Models:
There are 3 different types of small form factor MX devices.
- A standard MX which is a hardwired security device.
- MXxxW which is a security appliance which has a Wireless interface built in.
- MXxxC which is a security appliance with a built-in cellular interface and finally
- MXxxCW which is a security appliance that also has a wireless interface and a cellular interface built in.
The lower model numbers can service up to 50 users and the higher model numbers can service up to 200 users.
Small MX Model variations:
MX64(W) – 4 LAN ports, 2 WAN ports – 450Mbps Firewall Throughput
MX67(C/W/CW) – 4 LAN ports, 2 WAN ports – 450Mbps Firewall Throughput
MX68(C/W/CW) – 10 LAN ports, 2 WAN ports – 450Mbps Firewall Throughput
MX75 – 10 LAN ports, 3 WAN ports – 1Gbps Firewall Throughput
Large Form factor Models:
There are 6 different models of large form factor security appliances with the lower model numbers having fewer interfaces, slower throughput and supports smaller numbers of users as the model numbers increase so does the throughput and number of supported users.
Large MX Model Variations:
MX84 – Up to 200 users, 500 Mbps Firewall throughput, 5 WAN interfaces, 10 LAN Interfaces
MX95 – Up to 500 users, 2 Gbps Firewall throughput, 4 WAN interfaces, 6 LAN Interfaces
MX100– Up to 500 users, 750 Mbps Firewall throughput, 2 WAN interfaces, 10 LAN Interfaces
MX105 – Up to 750 users, 3 Gbps Firewall throughput, 4 WAN interfaces, 6 LAN Interfaces
MX250 – Up to 2000 users, 4 Gbps Firewall throughput, 2 WAN interfaces, 24 LAN Interfaces
MX450 – Up to 10000 users, 6 Gbps Firewall throughput, 2 WAN interfaces, 24 LAN Interfaces
Virtual Cloud Appliance:
There are 3 different models of vMX and these are small, medium or large. The virtual Cloud appliance is used to protect Private or Public Cloud infrastructure.
Small vMX – 200Mbps VPN Throughput
Medium vMX – 500Mbps VPN Throughput
Large vMX – 1 Gbps VPN Throughput
Smart Cameras
There are 10 models of smart cameras available, 3 are outdoor types and 7 are for indoor use.
Each model has an integrated Solid-State Drive for recording when there is no connectivity to the Meraki cloud.
Each model offers a different viewing angle or size of SSD and range from ceiling mounted cameras to wall mounted cameras.
The cameras offer a range of smart features such as number plate recognition and can correlate video events with access events for increased security.
IOT Sensors
Cisco Meraki IOT sensors gather environmental data or open and close events and feedback this data into the Meraki cloud.
This data can be used to trigger actions based upon certain events or measurements. There are 4 different types of IOT sensor currently available, and each model starts with the MT designation.
MT10 – Indoor Temperature and Humidity sensor
MT11 – Indoor Temperature probe sensor with multiple probe configurations available
MT12 – Indoor water leak detection probe
MT20 – Indoor open / Close sensor with 5 year battery life and tamper sensor.
How to setup and configure a Meraki device
Before a Meraki device can be configured you first need to claim ownership of the device and then it can be added to the Meraki dashboard for your organisation. To do this follow the steps below:
- Login to the Meraki dashboard
- Navigate to Organisation -> Inventory
- Click the claim button at the top right of the screen
- A box will appear where you can enter individual serial numbers of the devices that you want to add, or you can enter an order number and all devices within that order will be added to the inventory. Click claim when finished.
- Navigate to Network-Wide-> Configure -> Add Devices
- Select the claimed devices to add them to your existing network.
This process is identical for any Meraki device that you want to claim and add to the network.
How secure is a Cisco Meraki Firewall?
The Meraki MX Firewall, like all Meraki devices is a cloud-based device and the topic of how secure cloud applications are is a hotly debated topic with multiple different arguments for and against.
When comparing the MX series firewalls with Cisco NGFW, Palo Alto NGFW or Checkpoint Firewalls the MX has very similar scores with these leading Firewalls and great reviews from many satisfied customers.
The Meraki MX offers virtually all the same functions as non-cloud firewalls such as URL filtering, threat detection, Application visibility and control and antivirus and malware scanning.
Cisco Meraki also has a good reputation when it comes to securing their cloud services and proactively monitor and hunt for threats and vulnerabilities.
Cisco Meraki also market themselves as having the worlds most trusted and secure SD-WAN fabric which also integrates security technology from Cisco such as Umbrella and Talos.
How to export Cisco Meraki config and Export to another Meraki device
The configurations for all Cisco Meraki devices reside in the Meraki cloud and are not located on a physical machine.
This means that you are unable to export the configuration from the Meraki device to your computer.
Meraki does however have a very simple feature that can be used to clone the configuration from an existing device and add this configuration to a newly installed device such as a new switch or new access point.
This feature makes it extremely quick and easy to add new devices to the network and if they are powered up and connected correctly the configuration will take effect as soon as it has been applied in the Meraki dashboard.
Below is a summary of how to clone a configuration from a device.
- Log in to your organization in the Meraki dashboard and navigate to Switch > Switches.
- Tick the box next to the new device, which is the target for the configuration. Click edit then select clone from the drop-down menu.
- From the resulting menu select the existing switch that you want to copy the configuration from.
- Click Clone.
Once a configuration has been cloned to a device there is no way to roll it back, so it is important that the correct target device has been selected for the clone process.
What is Cisco Meraki used for?
Cisco Meraki devices are usually utilized in remote offices, small and medium business networks and outdoor areas that need network connectivity.
Since Meraki devices are fully controlled and configured from the Cloud dashboard, you don’t need to have physical access to the device. Also, they are suitable for customers and companies with limited number of IT and networking employees since everything is managed easily and centrally from the cloud interface.
Images Source: https://meraki.cisco.com/
Related Posts
- Introduction to Cisco EEM (Embedded Event Manager)
- Monitoring Cisco Network Infrastructure: What to Look for in an Ideal Cisco Monitoring Tool
- How to Reset Cisco Router or Switch to Factory Settings
- Comparison of LLDP vs CDP on Cisco Networking Devices
- Comparison of BGP Confederations vs Route Reflectors