In this article we will discuss the similarities and differences between the 3 “First Hop Redundancy” protocols supported by Cisco devices. These are Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP), Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) and Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP).
The main purpose of the above protocols is to provide redundancy to the default gateway (router or Layer3 switch) in a LAN environment.
Usually in a LAN we configure a default gateway IP on all users’ computers in order to reach the Internet (or other networks).
What if this default gateway (which is usually a router) fails? This means that Internet connectivity will be lost for the whole network. The protocols we will discuss here provide automated switchover of the default gateway IP address to a second routing device so that to have uninterruptible connectivity in case the primary device breaks down.
Although the above is the most commonly used scenario, we can also use HSRP/VRRP/GLBP in conjunction with some other mechanisms and protocols (such as BGP for example) to implement ISP redundancy (Dual WAN connectivity).
However in this particular article we’ll just discuss a simple implementation of providing redundancy to two routers in a LAN and provide comparison of VRRP Vs HSRP Vs GLBP which are supported by Cisco.
Let’s see a simple router network deployment in a LAN which will be used as the base to our discussion:
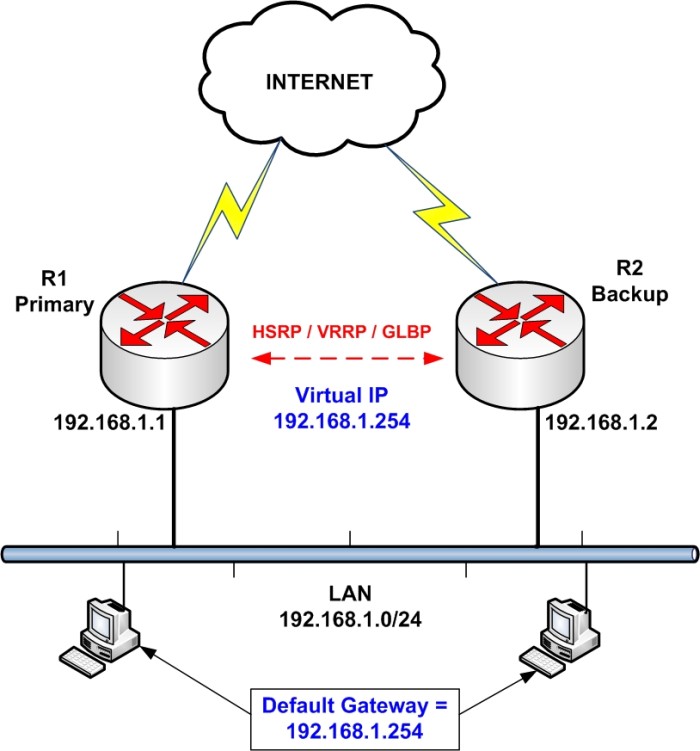
In our simple network above, we want to provide redundancy to the border routers (R1 and R2) which connect users to the Internet. By configuring one of the redundancy protocols (HSRP, VRRP, GLBP) we can achieve just that.
Each router has its own IP configured to its LAN interface (192.168.1.1 on R1 and 192.168.1.2 on R2). However, a Virtual IP (192.168.1.254) will also exist which will serve as the default gateway for the whole LAN. No matter which router is active or if we have one failed router, the Virtual IP will still exist in order to route packets from the users.
Basic Configuration of HSRP – VRRP – GLBP
Before moving into our comparison between the 3 protocols, let’s first see the basic configuration for each one:
HSRP Configuration
R1
interface Ethernet0/1
description LAN Interface of Active Router
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
standby 1 ip 192.168.1.254 <—- Create HSRP Group 1 and assign Virtual IP
standby 1 priority 101 <—- Assign priority above 100 to make this the primary router
standby 1 preempt <—- Makes router active if it has higher priority
R2
interface Ethernet0/1
description LAN Interface of Standby Router
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
standby 1 ip 192.168.1.254 <—- Create HSRP Group 1 and assign Virtual IP
standby 1 preempt <—- Makes router active if it has higher priority
VRRP Configuration
R1
interface Ethernet0/1
description LAN Interface of Active Router
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.254 <—- Create VRRP Group 1 and assign Virtual IP
vrrp 1 priority 101 <—- Assign priority above 100 to make this the primary router
vrrp 1 preempt <—- Makes router active if it has higher priority
R2
interface Ethernet0/1
description LAN Interface of Standby Router
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.254 <—- Create VRRP Group 1 and assign Virtual IP
vrrp 1 preempt <—- Makes router active if it has higher priority
GLBP Configuration
R1
interface Ethernet0/1
description LAN Interface of Primary Router
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
glbp 1 ip 192.168.1.254 <—- Create GLBP Group 1 and assign Virtual IP
glbp 1 priority 101 <—- Assign priority above 100 to make this the primary router
glbp 1 preempt <—- Makes router active if it has higher priority
glbp 1 load-balancing round-robin <—- Configure round-robin balancing of traffic
R2
interface Ethernet0/1
description LAN Interface of Secondary Router
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
glbp 1 ip 192.168.1.254 <—- Create GLBP Group 1 and assign Virtual IP
glbp 1 preempt <—- Makes router active if it has higher priority
glbp 1 load-balancing round-robin <—- Configure round-robin balancing of traffic
Comparison between HSRP Vs VRRP Vs GLBP
Now let’s move to the main purpose of this article: To see similarities and differences between the 3 protocols. I’ll just state briefly some comparison points below and then use a table to compare more features.
- HSRP and VRRP are very similar. Both have one active and one standby router at any given time.
- GLBP is the only one which provides load balancing of traffic among the devices in the group.
- HSRP and GLBP are Cisco proprietary.
- VRRP is an IETF standard (RFC 3768) so it is supported by all router vendors.
- If you have a mixed vendor environment (e.g Cisco, Juniper etc) than its better to use VRRP.
- All protocols support more than 2 routers in a group.
- All protocols support tracking. This means that you can track an interface of the router (or other network conditions) and if something goes wrong (e.g interface goes down or a destination tracked host does not respond) then a failover action is triggered.
- HSRP and GLBP support IPv6. The original VRRP does not support IPv6 but you need a special version of VRRPv3 for this.
Now let’s put some more comparison info in a table:
| HSRP | VRRP | GLBP |
| Cisco Proprietary | Standardized | Cisco Proprietary |
| Active and Standby mode only | Active and Standby mode only | Multiple routers pass traffic thus achieving load balancing |
| Must configure a separate IP for the Virtual. | Virtual IP can be same as physical IP of one of the routers | Must configure a separate IP for the Virtual. |
| Default priority = 100 | Default priority = 100 | Default priority = 100 |
| Higher priority (above 100) makes router active. Otherwise, higher IP makes router active. | Higher priority (above 100) makes router active. Otherwise, higher IP makes router active. | Higher priority (above 100) makes router primary forwarder. Otherwise, higher IP makes router primary forwarder. |
| Tracking supported (e.g interface state, routing info, reachability of remote host etc) | Tracking supported (e.g interface state, routing info, reachability of remote host etc) | Tracking supported (e.g interface state, routing info, reachability of remote host etc) |
| Supports IPv6 | No support for IPv6 on the original VRRP implementation. However, VRRPv3 (RFC 5798) now supports it. | Supports IPv6 |
| Supports timer and delay adjustments for failover | Supports timer and delay adjustments for failover | Supports timer and delay adjustments for failover |
Which one to Choose
If your network contains only Cisco devices, then I suggest to use HSRP. It works pretty well and is well supported. Now, if you have other vendors in your network or you are planning to install devices from other vendors in the future, then VRRP is the way to go.
Related Posts
- EIGRP Variance and Unequal Cost Load Balancing in Networking
- Comparison of Reported Distance vs Feasible Distance in EIGRP
- Explanation and Comparison of OSPF E1 vs E2 Routes
- Discussion and Explanation of OSPF Graceful Restart and Shutdown
- Explanation and Configuration of OSPF MD5 Authentication on Cisco Networks