This post will deal with creating Layer 2 VLANs on Cisco switches and performing all relevant configurations.
Up to 4094 VLANs can be configured on Cisco catalyst switches. By default, only VLAN 1 is configured on the switch, so if you connect hosts on an out-of-the-box switch they all belong to the same Layer 2 broadcast domain.
The need to configure several Layer 2 VLANs on a switch arises from the need to segment an internal Local Area Network (LAN) into different IP subnetworks.
If you want for example to separate the different departments of your enterprise into different IP subnetworks, then each department should belong to its own Layer 2 VLAN. For example, let’s assume the following scenario:
- Accounting Department: IP Subnet 192.168.2.0/24 –> VLAN 2
- Management Department: IP Subnet 192.168.3.0/24 –> VLAN 3
- Engineering Department: IP Subnet 192.168.4.0/24 –> VLAN 4
By separating the internal LAN into different IP subnets (and thus different VLANs) allows the network administrators to enforce traffic restrictions if needed between departments and have better control of internal hosts.
VLAN assignment on a switch is configured on a per-interface basis. That is, each switch port interface is assigned individually into a Layer 2 VLAN.
If you have more than one switch connected and you want the same VLANs to belong across all switches, then a Trunk Port must be configured between the switches.
The Trunk Port passes all VLANs between the switches. Let’s see the following network scenario to help us clarify some concepts.
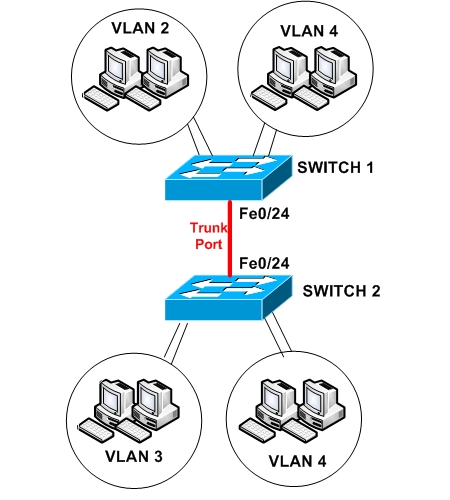
On the LAN network above, we have three VLANs. VLAN 2,3, and 4. VLAN 4 belongs both to SWITCH 1 and SWITCH 2, therefore we need a Trunk Port between the two switches in order for hosts in VLAN4 in Switch 1 to be able to communicate with hosts in VLAN4 in Switch 2.
The ports of the two switches shall be configured as following:
SWITCH 1:
Fe0/1 – Fe0/2 –> VLAN 2 (Accounting)
Fe0/10 – Fe0/11 –> VLAN 4 (Engineering)
Fe0/24 –> Trunk Port
SWITCH 2:
Fe0/1 – Fe0/2 –> VLAN 3 (Management)
Fe0/10 – Fe0/11 –> VLAN 4 (Engineering)
Fe0/24 –> Trunk Port
How to Create and Configure VLANs on Cisco Switches
Switch 1 Configuration:
! Create VLANs 2 and 4 in the switch database
Switch1# configure terminal
Switch1(config)# vlan 2
Switch1(config-vlan)# name Accounting
Switch1(config-vlan)# end
Switch1(config)# vlan 4
Switch1(config-vlan)# name Engineering
Switch1(config-vlan)# end
! Assign Ports Fe0/1 and Fe0/2 in VLAN 2
Switch1(config)# interface fastethernet0/1
Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 2
Switch1(config-if)# end
Switch1(config)# interface fastethernet0/2
Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 2
Switch1(config-if)# end
! Assign Ports Fe0/10 and Fe0/11 in VLAN 4
Switch1(config)# interface fastethernet0/10
Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 4
Switch1(config-if)# end
Switch1(config)# interface fastethernet0/11
Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 4
Switch1(config-if)# end
! Create Trunk Port Fe0/24
Switch1(config)# interface fastethernet0/24
Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
Switch1(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
Switch1(config-if)# end
Switch 2 Configuration:
! Create VLANs 3 and 4 in the switch database
Switch2# configure terminal
Switch2(config)# vlan 3
Switch2(config-vlan)# name Management
Switch2(config-vlan)# end
Switch2(config)# vlan 4
Switch2(config-vlan)# name Engineering
Switch2(config-vlan)# end
! Assign Ports Fe0/1 and Fe0/2 in VLAN 3
Switch2(config)# interface fastethernet0/1
Switch2(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 3
Switch2(config-if)# end
Switch2(config)# interface fastethernet0/2
Switch2(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 3
Switch2(config-if)# end
! Assign Ports Fe0/10 and Fe0/11 in VLAN 4
Switch2(config)# interface fastethernet0/10
Switch2(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 4
Switch2(config-if)# end
Switch2(config)# interface fastethernet0/11
Switch2(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 4
Switch2(config-if)# end
! Create Trunk Port Fe0/24
Switch2(config)# interface fastethernet0/24
Switch2(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
Switch2(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
Switch2(config-if)# end
Verification
If you want to verify that the physical interfaces are assigned properly to each VLAN, then run the following show commands:
SWITCH1#show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8
Fa0/9, Fa0/12
Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15
2 Accounting active Fa0/1, Fa0/2
4 Engineering active Fa0/10, Fa0/11
SWITCH2#show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8
Fa0/9, Fa0/12
Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15
3 Management active Fa0/1, Fa0/2
4 Engineering active Fa0/10, Fa0/11
Communication Between VLANs
Now, after separating the network into different VLANs, this means that we have created separate broadcast domains (one for each VLAN) and now hosts within the same VLAN can freely communicate between them (provided they belong also in the same Layer 3 subnet).
On the other hand, hosts that belong in different Layer 2 VLANs can’t communicate between them. e.g hosts in VLAN 3 are not allowed to communicate with hosts in VLAN 4.
If you want to provide communication between hosts in different VLANs, then there must be a Layer 3 engine in the network (either a router or Layer 3 switch). In this article I have described how inter-vlan routing is configured on Layer 3 switches.
Related Posts
- How Does a Network Switch Learn MAC Addresses?
- How to Find a Device MAC Address on a Cisco Switch (show mac address-table)
- How to Configure a Loopback Interface on Cisco Router & Switch
- Cisco Switch Layer2 Layer3 Design and Configuration
- Description of Switchport Mode Access vs Trunk Modes on Cisco Switches