In the previous post, we have discussed about isolating traffic using the private VLAN feature at Layer2 level. In this tutorial, we will discuss traffic isolation at Layer3 level using VRF Lite on Cisco routers.
What is VRF Lite
VRFs employ essentially the same concept as VLANs and Trunking, but at Layer 3.
VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) is traditionally associated with IP MPLS technology whereby an ISP creates Layer3 (or Layer2) VPNs for customers using VRF.
Consider a VRF as a separate routing instance (and separate routing table) on the same network device holding the IP routes for each customer which are isolated from the other customers.
Each VRF is like a separate virtual router with its own routing table on the same physical router.
If you don’t work in an ISP environment you will not encounter this technology very often. Also, from what I know, MPLS and VRFs are not examined at the CCNA or CCNP R&S level.
They are discussed in the chapters needed for your CCIE R&S certification. If you want to read about this technology, one good book to start with is MPLS Fundamentals wrote by Luc De Ghein.
Now, although VRFs and MPLS are usually configured on high-end ISP routers, you can still use this feature on some smaller Cisco ISR routers in a simplified manner called VRF Lite and have the same advantages.
With VRF Lite, you can have separate routing tables on the same physical router device. Each routing table (VRF instance) is isolated from the other VRF instances.
To demonstrate how to use this feature lets see the following simplified scenario:
Network Scenario using Cisco 891 and VRF Lite
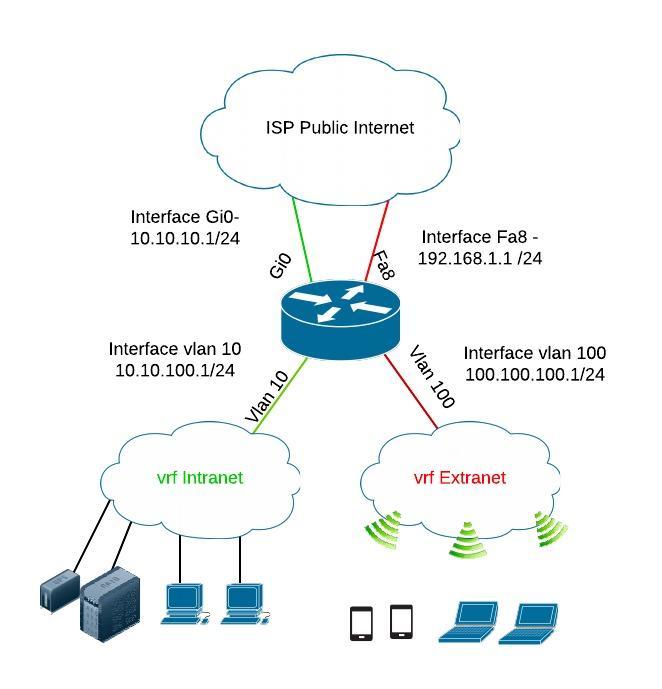
Consider the scenario depicted on the diagram above. We have a Cisco 891 border router with an Intranet connection for employees’ computers and company servers and also we need to offer internet connectivity for a Wi-Fi connection to allow guests to connect to the internet.
The company security team demanded that the Wi-Fi connection must be totally separated from the local intranet network, so that guests don’t have access to the local network. Therefore we can isolate the two Layer3 networks using VRF Lite. We will create “VRF Intranet” and “VRF Extranet” for the two networks.
Configuration Example on Cisco Router
The router used is CISCO891-K9 with image c890-universalk9-mz.151-4.M4.bin installed.
Each VRF Instance will have two Layer3 routed interfaces associated with it as shown below. Consider each VRF Instance as a virtual router with two interfaces.
- VRF Intranet: VLAN10 and Interface Gi0 will be included in “vrf Intranet”.
- VRF Extranet: VLAN100 and Interface Fa8 will be included in “vrf Extranet”.
Step 1 : Create the VRF Lite Instances
ip vrf Extranet
description Extranet
!
ip vrf Intranet
description Intranet
!
Step 2 : Configure VLANs and interfaces and include them in the VRF instances
vlan 10
name Intranet
!
vlan 100
name Extranet
!
interface GigabitEthernet0 <————– wan port facing the internet for Intranet traffic
ip vrf forwarding Intranet <———— interface is attached to the Intranet VRF
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Vlan10 <—————— SVI interface for Intranet traffic
description Intranet <—————— interface is attached to the Intranet VRF
ip vrf forwarding Intranet
ip address 10.10.100.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet8 <—————— wan port facing the internet for guest traffic
ip vrf forwarding Extranet <—————— interface is attached to the Extranet VRF
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Vlan100 <—————— SVI interface for Extranet traffic
description Extranet
ip vrf forwarding Extranet <—————— interface is attached to the Extranet VRF
ip address 100.100.100.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0 <—— on this interface connect the WiFi Access Point for guests
description AP
switchport access vlan 100
no ip address
!
interface FastEthernet1 <—— on this interface connect Intranet hosts
description Intranet
switchport access vlan 10
no ip address
!
Step 3 : Add default routes facing the internet for both VRF instances
ip route vrf Intranet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.254
ip route vrf Extranet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.254
Step 4 : Verifications
– showing the vrf configuration
Networkstraining#sh run vrf Intranet
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 324 bytes
ip vrf Intranet
description Intranet
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0
ip vrf forwarding Intranet
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Vlan10
description Intranet
ip vrf forwarding Intranet
ip address 10.10.100.1 255.255.255.0
!
ip route vrf Intranet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.254
end
Networkstraining#sh run vrf Extranet
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 326 bytes
ip vrf Extranet
description Extranet
!
!
interface FastEthernet8
ip vrf forwarding Extranet
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Vlan100
description Extranet
ip vrf forwarding Extranet
ip address 100.100.100.1 255.255.255.0
!
ip route vrf Extranet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.254
– verify both routing tables
Networkstraining#sh ip route vrf Intranet
Routing Table: Intranet
Gateway of last resort is 10.10.10.254 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.10.10.254
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.10.10.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0
L 10.10.10.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0
Networkstraining#sh ip route vrf Extranet
Routing Table: Extranet
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.1.254 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.1.254
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet8
L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet8
– verify ARP entries
Networkstraining#sh ip arp vrf Intranet
Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface
Internet 10.10.10.1 – fc99.4712.9ee3 ARPA GigabitEthernet0
Internet 10.10.100.1 – fc99.4712.9ecb ARPA Vlan10
Internet 10.10.100.10 5 cce1.7f79.48f2 ARPA Vlan10
Networkstraining#sh ip arp vrf Extranet
Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface
Internet 100.100.100.1 – fc99.4712.9ecb ARPA Vlan100
Internet 100.100.100.100 5 001c.0fdc.de41 ARPA Vlan100
Internet 192.168.1.1 – fc99.4712.9ed3 ARPA FastEthernet8
Final Notes
- As you can see, the routing tables are totally separated and the traffic will be totally separated.
- If you run the command “show ip route” without specifying a VRF name, it will show the “Global Routing Table” of the device (which will be empty in our example above).
- When you issue ping, telnet or other commands that make us of the routing tables, you must always specify the VRF routing instance name that you want to use:
Example: ping vrf Intranet 10.10.100.10
- The VRF Lite feature is offered by other vendors as well. For example in Juniper environment it is called “routing instance”.
Cisco ASA VRF Support
Many people are asking if the Cisco ASA firewall supports VRF configuration. The answer is that the ASA does not support vrf configuration as there is only a single routing table instance on the ASA.
Here are the options that you have to use an ASA device in a VRF network:
- Configure VLAN subinterfaces on the ASA and terminate each VRF network on each subinterface. Then you can apply access control lists and traffic control of the inter-vrf communication via the ASA appliance.
- Using security contexts: This means configuring different security contexts (virtual ASA firewalls) on the same device thus having separate routing tables and separate policy control for each context. This is similar to having multiple VRFs on the same appliance however its not a native VRF functionality like the one you have on Routers.
DOWNLOAD ARTICLE AS PDF FILE
Related Posts
- Introduction to Cisco EEM (Embedded Event Manager)
- Monitoring Cisco Network Infrastructure: What to Look for in an Ideal Cisco Monitoring Tool
- How to Reset Cisco Router or Switch to Factory Settings
- Comparison of LLDP vs CDP on Cisco Networking Devices
- Comparison of BGP Confederations vs Route Reflectors