As a network engineer, you will be spending almost half of your time in troubleshooting issues arising in the network or solving problems related to IT and network conditions.
Although there are several Windows or Linux commands that you can use on host computers to check for various connectivity issues, a professional should have a number of additional software tools in his/her “toolbox” that can be used to troubleshoot a variety of different network conditions.

When users start blaming the network for slow internet connection, slow transferring to the file or backup server, no connection to the internal domain servers etc, a network administrator must be able to figure out fast what the actual problem really is.
Below I have collected some network troubleshooting tools that you should know about if your job is to manage an IT or network infrastructure in an enterprise environment.
Some of them are just simple utilities or operating system commands that you already have installed on any windows or Linux host.
Of course the tools below will be much more effective when used in conjunction with other management and monitoring software suites that provide a holistic view in the whole network environment.
PingPlotter
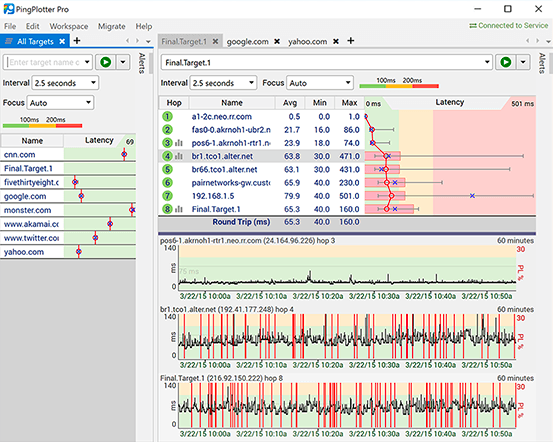
PingPlotter is a utility that troubleshoots network issues from a single machine. It can be installed and run on Windows or Mac computers and is available in 3 editions:
- Free
- Standard Edition ($39.99 Perpetual License or $6.99 monthly subscription)
- Professional Edition ($349 Perpetual License or $29 monthly subscription)
Using a unique combination of traceroute, ping, and whois, the program tracks network data over time that can be exported and analyzed to identify issues with the network (over time), performance problems etc.
This data can be analyzed within the program to allow network engineers to determine the source of possible network interruptions that happened. This means that you have a history of the health of your network.
Data is shown graphically, as is each hop, to make it obvious where a problem exists! Basically you set “Targets” that you want the tool to track which will set the tool to start collecting data about the path to the target.
OpManager
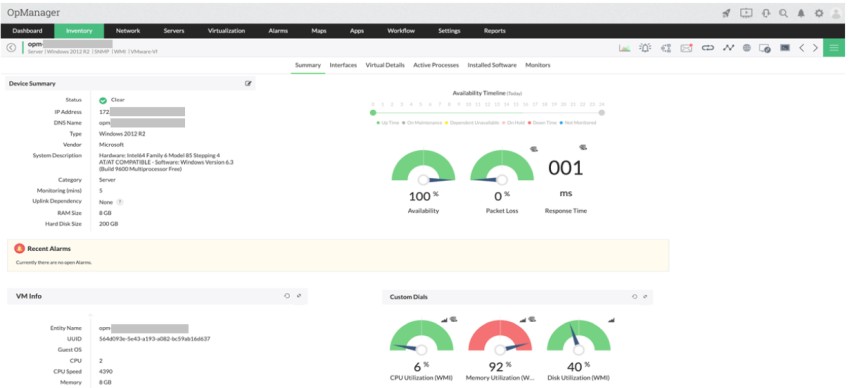
I know that free tools for troubleshooting a network are great for low budget operations, but for a professional enterprise network environment, you need something more comprehensive.
OpManager is a solution from ManageEngine that offers a holistic toolset for monitoring and troubleshooting networks of any size and in any location.
Although it includes several well known troubleshooting tools (such as Ping (ICMP/ SNMP/ Proxy), Tracert/ Traceroute, Browse, Telnet/ SSH, Remote Desktop, Terminal etc), what I like best is the IT workflow automation.
IT workflow automation is a powerful and efficient tool for network troubleshooting automation, capable of executing Level 1 troubleshooting and repetitive maintenance tasks based on predefined workflows.
A professional network administrator can seamlessly integrate actions into the workflow builder using a drag-and-drop feature, enabling the creation of a step-by-step troubleshooting flow. This facilitates regular identification and resolution of network faults, triggered either by scheduled time intervals or alarms on associated devices or groups.
TotalView

TotalView is an “all-in-one” solution for network monitoring and troubleshooting. It proactively alerts IT administrators when there is a significant issue.
Rather than just giving a generic warning, TotalView gives a “plain English” description of the exact location and cause (if known) of the issue on the network.
The program even accounts for Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It also allows administrators to monitor the cloud services their company pays for to ensure that the company is getting its money’s worth.
It has countless additional features, such as the identification of and option to block devices that have unpatched vulnerabilities and a visual network path monitor.
It supports a multitude of vendor infrastructures including Cisco, Juniper, Aruba, F5, Linksys. HP, Arista and many more.
Cisco Network Assistant
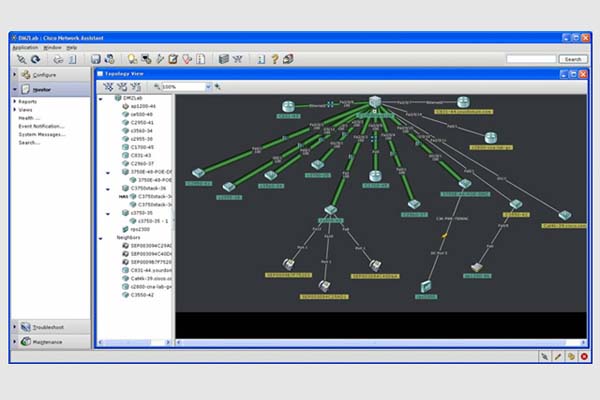
Coming from network giant Cisco, this tool serves as a free network monitoring utility and supports up to 80 devices.
Especially useful for network admins who already use Cisco network devices, it also allows access to Cisco’s “Active Advisor” offering important information on monitored devices, such as those with firmware versions that are too old or out of support.
Firmware update and common operations can be performed on all devices connected to the network simultaneously, as well.
It also has configurable network alarms and diagnostic information that helps administrators get to the bottom of network problems.
It doesn’t provide the same “plain English description”, but any network professional should be able to take information from the utility and figure the issue out in a fairly short amount of time.
The tool supports Cisco routers, switches, wireless controllers and access points which are shown on a nice visual map with all their interconnection links.
Netfort LANGuardian
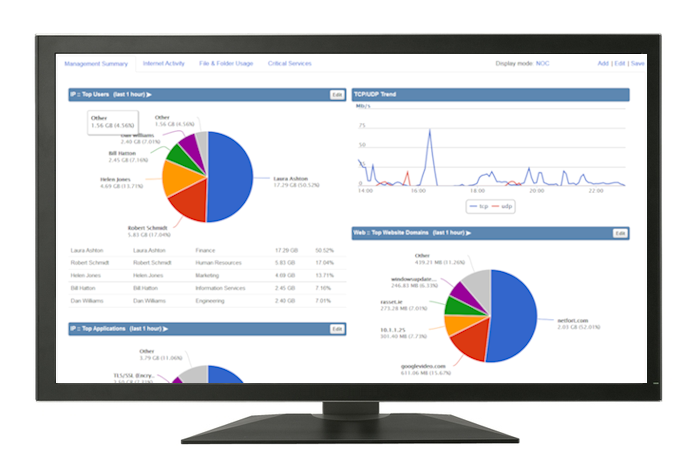
LANGuardian is a tool that allows network administrators to “drill down” to very specific information impacting a network since the tool allows deep-packet inspection of the network traffic.
First, admins can view activity on the WAN and LAN, and then drill down to individual devices and users to easily weed out who is hogging the bandwidth!
Administrators can even review individual data transfers after the fact. This is one of the few tools that integrates with Active Directory.
This allows specific network-based actions to be recorded with both the name of the user logged in and the device’s name on the network.
Finally, the utility also shows network engineers improvements that can be made and ports and protocols that can be blocked in a manner that still allows legitimate business traffic but optimizes the network by blocking activities that are already banned.
Since the tool inspects the actual packets traversing your network, it can also identify security attacks such as ransomware or intrusion attempts.
Its pricing is based on licensing according to number of users and the number of sensors you want to install.
Wireshark
Arguably the world’s most popular protocol analyzer, Wireshark is free to use. It has a bit of a sharper learning curve than some network analyzers, but once a network administrator becomes proficient, Wireshark becomes an invaluable tool in troubleshooting network problems.
In conjunction with WinPcap, Wireshark can “sniff” packets from the network and produce very detailed logs of live traffic that can be filtered from within the program and drilled down to individual devices and users.
Wireshark also stands out because it’s open source and runs on every major operating system and can analyze packets extracted by just about any other protocol analyzer!
Literally everything, from a high-level live network view, to what time a specific user on a specific machine downloaded a prohibited file, can be inspected with Wireshark.
Tamos Throughput Tester
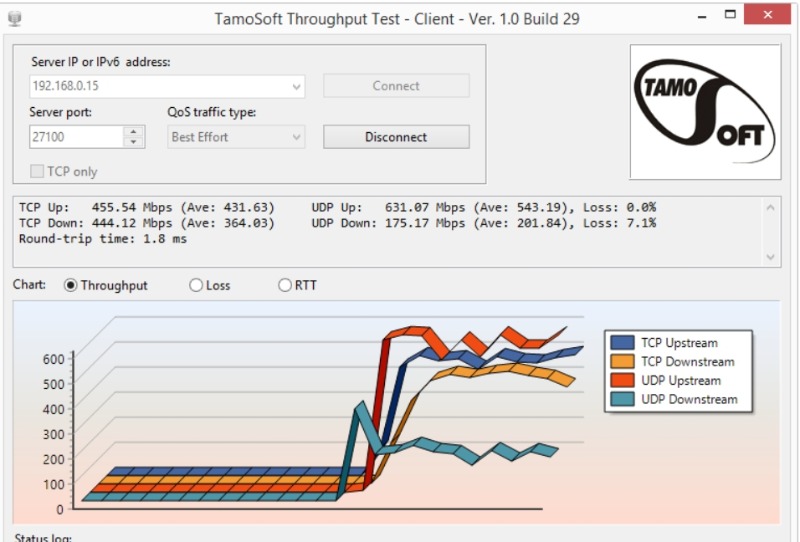
This diagnostic utility is designed to be run when your network is not being used. A “server” that sends data and a “client” that receives it must be configured.
The program tests the bandwidth your network is capable of handling by sending lots of UDP and TCP packets and measures throughput, packet loss etc (just like other packet generators do).
The utility then outputs a full report on upstream and downstream speed, packet loss rate, and a general performance evaluation.
Network engineers can use this to determine whether new equipment or simply bigger links are required. Tamos also offers a paid utility that performs similar operations, just over WLAN.
Ping
Ping is the simplest and one of the most effective troubleshooting tools available. It is included in every Windows and Linux machine or in many other networking devices such as routers, firewalls etc.
Basically, it sends ICMP packets to a destination and waits to see if an ICMP reply is received from the destination target.
If an ICMP reply is received from the target, it means first that the target host is alive and also that the network path from the source to the destination in also available.
One of the most useful options in Ping that I use a lot when troubleshooting a network is to send ICMP packets continuously using the “-t” option as shown below:
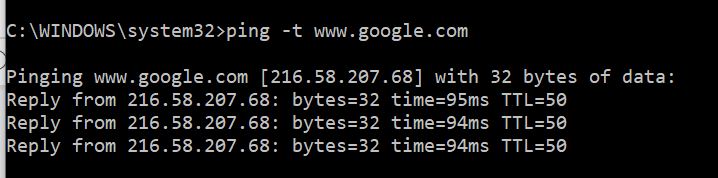
When I’m doing changes in a network (e.g changing routing configuration, replacing links, upgrading routers etc), I always have a Ping command running continuously from a source to a destination in order to observe when the network path will be up or down.
Trace Route
This is another networking utility available on both Windows and Linux OS machines. On Windows, the command is “tracert” and on Linux the command is “traceroute”.
This is a useful command when you want to see all the hops a packet takes in a path between source and destination.
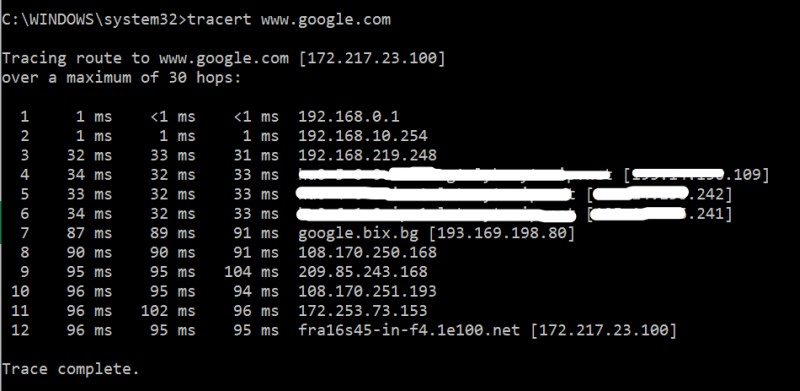
The command sends 3 packets so it displays the times of each packet (in ms) between each hop.
The command is useful if you have a network with multiple links towards a destination (e.g you might have two links with two ISPs) and you want to see which link/ISP is actually used towards the Internet.
Nslookup
Another networking related utility available as a command on Windows and Linux machines.
Its main purpose is to troubleshoot DNS related issues. The basic function of nslookup is to find out the mapping between Domain Names to IP addresses or vice-versa by querying a DNS server.
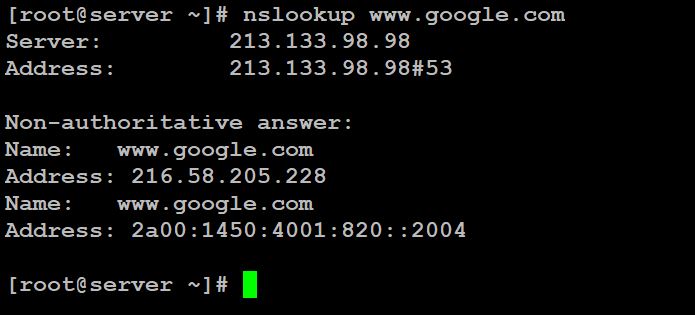
As shown on the picture above after running “nslookup www.google.com” we get back two IP addresses for Google (one IPv4 and one IPv6).
Nmap
I have talked extensively about Nmap in the articles here and here (if you want to learn more details about this powerful networking tool). Moreover, in the article here I’m explaining how to use Nmap in host discovery and penetration testing.
Although the tool is mainly used in security assessments, I use it also extensively in network troubleshooting as well.
Here is a practical scenario that I encounter many times: A server administrator has just installed a shiny-new Web Server machine in a DMZ zone behind a firewall.
He calls and complains that his machine is not accessible from the Internet. What I do here is to run Nmap from the Internet to scan the IP address of the Web server (for port 443 or 80).
If Nmap does not show the ports above as “open” then it means that probably the firewall administrator has not allowed these ports yet.
So, there you have it. These network troubleshooting tools can be really useful for a network or IT admin and combined with your troubleshooting skills they can make your life easier in your job environment.
Related Posts
- Unveiling the Significance of Network Automation in Contemporary Networking
- Comparison of GNS3 vs EVE-NG vs Packet Tracer for Networks Simulation
- 5 Best Practices to Keep Rogue Devices at Bay
- EIGRP Variance and Unequal Cost Load Balancing in Networking
- Classful vs Classless IP Addressing – Comparison and Differences
