The Cisco 800 series routers are part of the “Branch Office” category, used mainly for SOHO purposes or for connecting remote branch offices to a central location. They are “fixed hardware configuration” devices, meaning that they don’t have any plug-in hardware slots for inserting additional interfaces to the device (all the interfaces are fixed).
All the 800 series models come with a 4-port 10/100 managed switch used for connecting the internal LAN computers, and with an IOS software that supports security features including the Firewall set.
The main difference of each model is the WAN interface. All models that end with “1” in the model number (i.e 851, 861, 871, 881, 891) have a 10/100 Fast Ethernet interface as a WAN port.
The other models have an xDSL type WAN port (i.e ADSL, G.SHDL, VDSL2). Also, all models have the option of a WiFi Radio interface (the model number ends with a “W”, e.g 851W, 857W, 861W etc).
In this post I will describe a basic configuration scenario for connecting a Cisco 800 router for Internet access. I will use a model with an Ethernet WAN interface (such as 851, 861, 871, etc) since those models are the most popular.
Something to have in mind for all 800 series routers, the four LAN interfaces (FE0 up to FE3) are Layer2 switch interfaces that are assigned by default to Vlan1.
This means that you can not assign an IP address directly to the LAN interfaces. The IP address for the LAN-facing side of the router is assigned under “interface Vlan1”.
On the other hand, the WAN interface (FE4) is a normal Layer3 router port, which means you can assign an IP address directly on the interface (“interface FastEthernet4”).
I will describe three basic scenarios which are frequently encountered in real networks.
- Scenario 1: WAN IP address of router is assigned dynamically by the ISP. LAN IP addresses assigned dynamically from the router to the internal PCs.
- Scenario 2: WAN IP address of router is static. LAN IP addresses assigned dynamically from the router.
- Scenario 3: WAN IP address of router is static. An internal LAN Web Server exists. The router performs a static Port NAT (port redirection) to forward traffic from Internet towards the internal Web Server.
Scenario 1:
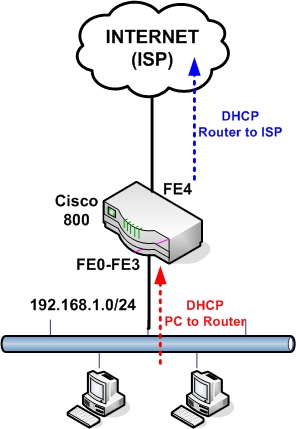
Configuration:
The following is the basic configuration needed for the simple scenario above.
configure terminal
enable secret somesecretpassword
! Configure the DHCP pool to assign addresses to internal hosts
ip dhcp pool vlan1pool
network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 192.168.1.1
dns-server 100.100.100.36
! Do not assign addresses 1 to 30
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.30
! This is the LAN facing interface of the 800 router. Used as gateway for PCs
interface vlan 1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
no shut
! Interfaces FE0 to FE3 are Layer 2 interfaces
interface FastEthernet0
no shut
interface FastEthernet1
no shut
interface FastEthernet2
no shut
interface FastEthernet3
no shut
! This is the WAN interface getting address via DHCP from the ISP
interface FastEthernet 4
no shut
ip address dhcp
ip nat outside
! Configure NAT. All internal hosts will be nated on the WAN interface
ip nat inside source list 1 interface fastethernet4 overload
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 fastethernet4
line vty 0 4
password somestrongpassword
Scenario 2:
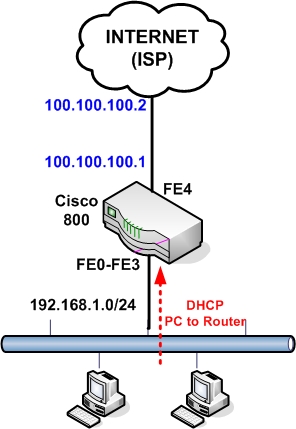
Configuration:
This is the same configuration as scenario 1 except that the WAN IP address is static and also the default gateway of our ISP is known.
The only difference from the configuration above is on the WAN interface and on default route:
! This is the WAN interface with static IP
interface FastEthernet 4
no shut
ip address 100.100.100.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat outside
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 100.100.100.2
Scenario 3:
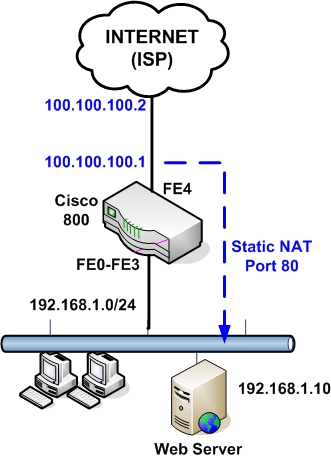
Configuration:
Here the WAN address is static and we have also an internal Web Server for which we need to allow HTTP access from Internet. To do this we must configure a static NAT with port redirection. Traffic that comes towards our WAN public address 100.100.100.1 on port 80 will be redirected by the router to the internal Web Server at address 192.168.1.10 on port 80.
configure terminal
enable secret somesecretpassword
! Configure the DHCP pool to assign addresses to internal hosts
ip dhcp pool vlan1pool
network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 192.168.1.1
dns-server 100.100.100.36
! Do not assign addresses 1 to 30
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.30
! This is the LAN facing interface of the 800 router. Used as gateway for PCs
interface vlan 1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
no shut
! Interfaces FE0 to FE3 are Layer 2 interfaces
interface FastEthernet0
no shut
interface FastEthernet1
no shut
interface FastEthernet2
no shut
interface FastEthernet3
no shut
! This is the WAN interface with static IP
interface FastEthernet 4
no shut
ip address 100.100.100.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat outside
! Configure NAT. All internal hosts will be nated on the WAN interface
ip nat inside source list 1 interface fastethernet4 overload
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
! Configure static NAT for port redirection
ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.1.10 80 100.100.100.1 80 extendable
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 100.100.100.2
line vty 0 4
password somestrongpassword
DOWNLOAD ARTICLE AS PDF FILE
Related Posts
- EIGRP Variance and Unequal Cost Load Balancing in Networking
- Comparison of Reported Distance vs Feasible Distance in EIGRP
- Explanation and Comparison of OSPF E1 vs E2 Routes
- Discussion and Explanation of OSPF Graceful Restart and Shutdown
- Explanation and Configuration of OSPF MD5 Authentication on Cisco Networks