TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are both Layer 4 transmission protocols in the OSI model. However, these two protocols are quite different. From a high level view you could say that TCP is reliable and UDP is unreliable. Why then would we use UDP?
UDP Characteristics
Due to UDP being able to tolerate loss, this provides for low latency. This is extremely useful for video streaming, live audio, and other applications requiring live data.
UDP is often referred to as a connectionless protocol. Unlike TCP, it does not require a session to be opened prior to, or during, the transmission of data.
This will often be called “best effort” transmission. Two network end-points that communicate via UDP start sending packets between them without first arranging any connection details.
TCP Characteristics
For things such as the transferring of files, downloading of webpages (internet browsing), sending/receiving email messages, connecting remotely to other machines etc, we use TCP.
This is because TCP establishes a connection before and during the transmission of data which prevents packet loss. The result of this may be a bit slower than UDP, but it also means all data will arrive at the destination reliably.
So why wouldn’t TCP work for video? Wouldn’t it be a good thing to have lossless video? The answer to this is that yes in theory that would be a good thing, but in reality it would not work very well.
TCP relies on a handshake process, windowing, and verification to effectively send its data without loss. The small delays this would cause are enough for video quality to suffer.
Quick Comparison Table
| TCP | UDP |
| Connection oriented | Connectionless |
| Reliable | Unreliable |
| Slower | Faster |
| Higher header overhead | Lower header overhead |
| Extensive error checking mechanisms | Very basic error checking |
| Sequencing of data packets | No sequencing of data packets |
| Re-transmission of lost packets | No re-transmission |
TCP 3-way handshake vs UDP Connectionless Communication
TCP relies on a 3-way handshake to establish a connection with the destination before sending data.
This process consists of three basic steps:
- First, the sender sends a SYN (Synchronize Sequence Number).
- Next, the receiver replies to the SYN with a SYNACK. This includes an ACK signaling that the SYN was received and the SYN tells the sender which sequence number it expects to begin the transfer with.
- Finally one last ACK is sent to the receiver letting it know the SYNACK was received properly. At this point a connection is established and data transfer may proceed.
Compare the three-way handshake process with that of UDP. There is no connection established with UDP. It can take different paths outbound vs. inbound. It can have small amounts of loss and the sender does not care whether the receiver gets all its information.
This is the very reason that there is less information in the header resulting in less bandwidth overhead and faster speeds.
TCP Vs UDP Headers
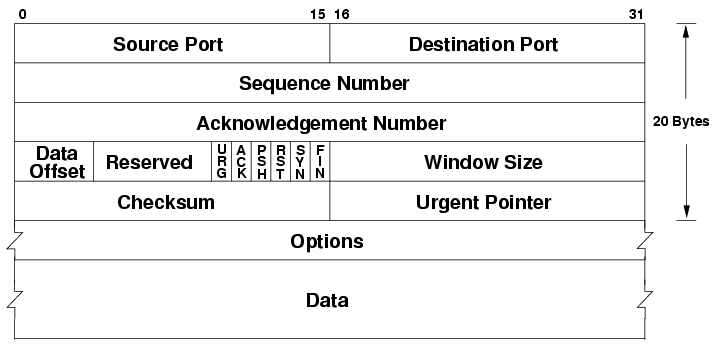
TCP Header
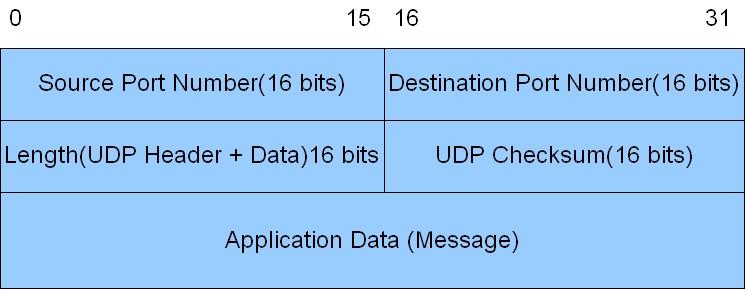
UDP Header
You may be wondering how one protocol can have more bandwidth overhead than the other. If the data being transmitted is the same amount then surely there wouldn’t be a difference right?
You would be wrong and the reason being is that the headers are different from each other with TCP having a much larger packet header as shown from the diagrams above.
TCP and UDP require that they encapsulate the data packets they are sending with their own headers as a way to tell the information how it is to be transmitted.
Both TCP and UDP have some commonalities in their packet headers. They both have source and destination ports as well as checksums to look at whether any data was lost in transmission.
What is more interesting are the differences. The only other thing UDP has is a “Length” field telling the recipient how much data is in the packet so it knows how long to wait for the information. TCP however, has many more fields.
TCP has fields for SYNs and ACKs which we have already discussed. It also has a section of the header reserved for control flags such as resetting the TCP connection when it realizes it is transmitting too fast.
Also included is the urgent pointer field which is usually ignored, but in combination with one of the control flags, it can be used to mark a message as requiring priority processing.
Perhaps most importantly is the windowing field. This field says how much data may be transferred before an ACK is required. Too small a data field leads to unnecessary slowness. Too large a field and there could be data loss.
Windowing allow the packets to grow in size until a limit is reached for loss. Perhaps you have noticed that downloads always begin slowly and seem to speed up after a while.
Example of Protocols using TCP
- HTTP / HTTPs (ports 80, 443)
- SSH (port 22)
- FTP (port 21)
- Telnet (port 23)
- Email SMTP (port 25)
- Remote Desktop Protocol – RDP (port 3389)
Example of Protocols using UDP
- DNS (port 53)
- Trivial File Transfer Protocol – TFTP (port 69)
- Network Time Protocol – NTP (port 123)
- Real Time Protocol (random UDP ports)
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, although TCP and UDP both ride over IP, they transmit very differently. TCP is slower, yet more reliable which is great for communication that cannot tolerate loss.
UDP on the other hand is much faster, has less bandwidth overhead, and can tolerate more loss. Due to this it is not a good solution for files that need to arrive intact. One is not better than the other, but they are definitely better at different things.