In this article we’ll discuss and examine the Syslog Protocol which runs over its default UDP port 514 (or the secure TCP port 6514), and also describe the characteristics and usefulness of Syslog in networks.
All computer systems and network devices generate a historical record of events that take place on the device. This record of events is called a log file and is usually saved as a text file in the device storage or just temporarily stored inside the RAM of the device.
The log file is useful to an Administrator when troubleshooting problems with the device because they can see all the events which took place at a certain time and date.
If the Administrator looks after a very large network with hundreds of devices, then this troubleshooting can become very difficult especially if it is not known which device has caused the problem or if many devices are having problems.
In this scenario the log file on each device will need to be checked individually and some log files can contain thousands of lines of output.
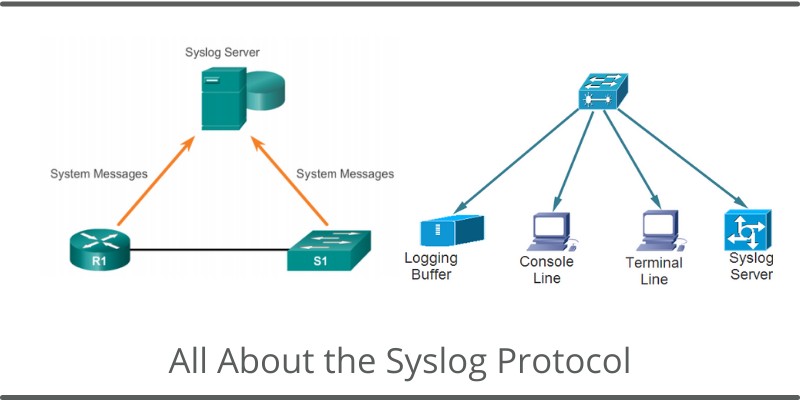
The syslog protocol is used to transfer these log messages from devices to a central server (syslog server) in order to be able to store them for a long period and analyse them efficiently.
What is the default syslog protocol port? (UDP 514)
By default, syslog protocol works over UDP port 514. If you need to pass syslog packets through a firewall, you need to allow access at UDP 514.
What is the secure syslog port? (TCP 6514)
If you send syslog over the default UDP port, then messages are un-encrypted and can be intercepted and stolen over the network. If you want secure log messages transfer, then Syslog must work over TCP 6514 with secure TLS certificate-based authentication (RFC 5425).
What is a syslog server used for?
A Syslog Server is an application running on a computer that collects and organizes all of the log files sent from the various devices on a network.
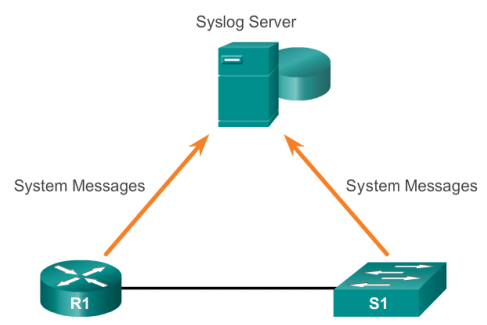
When an event takes place on a device, this device will write the event to its own log file and then it will send a copy of the event to the syslog server using the syslog protocol as discussed above.
The syslog protocol is the method that is used to process, package and transport the event logs to the central syslog server.
On the Syslog server an Administrator can see all the collated logs from every device on their network in one place and in an organised manner.
Depending on the features of the installed syslog program, they can manipulate this information to make it easier to understand by filtering the information by date, by device type or by searching for certain keywords. Logs can also be colour coded by severity or device type.
Is Syslog TCP or UDP protocol?
The syslog protocol is defined in RFC 5424 and is used to transport messages from devices to the syslog collector over IP networks.
The protocol uses the connectionless transport protocol UDP by default over port 514. Alternative port numbers and TLS can be used instead of UDP however, it is highly recommended to use the default port over UDP as this protocol has less network overhead.
If security is a concern, then secure syslog can be implemented. Secure syslog uses SSL / TLS to encrypt the IP packets using a certificate before they are sent across the IP network to the syslog collector. Secure syslog uses TCP over port 6514.
Syslog Message Format
A syslog message consists of three parts. The first part is the HEADER, the second part is called the Structured-Data (SD), and the third is the message (MSG).
Inside the Header we have the PRI field which contains a numerical code which indicates the severity of the message. There are 8 severity levels which range from 0 to 7.
- 0 – Emergency: system is unusable
- 1 – Alert: action must be taken immediately
- 2 – Critical: critical conditions
- 3 – Error: error conditions
- 4 – Warning: warning conditions
- 5 – Notice: normal but significant condition
- 6 – Informational: informational messages
- 7 – Debug: debug-level messages
The HEADER is made up of the following fields:
- PRI – Priority value (severity)
- Version – The version of syslog protocol
- Timestamp – The time the event was recorded
- Hostname – The Hostname, Ip Address, FQDN of the device which is sending the log
- Application – Identifies the device or Application where the message originated
- Process id – Used by some log collectors to identify anomalies
- Message id – Identifies the type of message.
The MESSAGE field contains a standard Unicode text output which details what event has taken place.
There are several syslog servers which are available for free such as Kiwi syslog server, PRTG or the program TFTPD32 also contains a basic Syslog server.
More advanced Syslog servers are usually found bundled with Network Management Applications such as Cisco Prime Infrastructure or SolarWinds.
How to configure syslog on a Cisco device
To allow a Cisco switch or router to send its logs to a central syslog server the following configuration will need to be completed on the switch:
enable
configure terminal
logging buffered 8192
logging host <IP Address of syslog server>
Note: The number 8192 shows how many bytes to reserve in memory for the log messages.
To limit the level of logging which is sent the severity level of the log message needs to be configured.
logging traps 5
end
What is syslog level 7?
The severity level of 7 will cause the switch to send debugging messages and messages from all the previous levels 0 – 6 as well.
It is only recommended to use a logging level of 7 when troubleshooting a particular problem and to not leave it running all the time as this level of logging will raise the CPU usage and could cause the switch or router to slow down its throughput of traffic.
The standard level of logging which is used in most scenarios would be a logging level of 4. This would cause all Warning, Error, Critical, Alert and Emergency messages to be logged and sent to the syslog server.